How to turn your Ubuntu 14.10 headless server into a XFCE + VNC Network Desktop
This tutorial describes the installation of Gnome 3, XFCE and VNC on a headless server (server without monitor) to turn it into a Linux Desktop that you can access from anywhere over the internet with VNC. The server that is used for this setup is a root server in a datacenter that runs just a minimal Ubuntu 14.10 operating system. I will guide you trough the installation and configuration of the following software:
Ubuntu 14.10
Gnome 3.14
VNC 4.1.1
Important Notes: This procedure is only applicable to a new installed Ubuntu Linux OS, if you have existing running Ubuntu Linux with a different version where you like to install a desktop and vnc, i suggest you make a backup of your system and after that, you may proceed with this procedure. All commands below assume that you are logged in as root user, so please run "sudo -" to become root if you are logged in as a different user.
Gnome 3.14
VNC 4.1.1
Important Notes: This procedure is only applicable to a new installed Ubuntu Linux OS, if you have existing running Ubuntu Linux with a different version where you like to install a desktop and vnc, i suggest you make a backup of your system and after that, you may proceed with this procedure. All commands below assume that you are logged in as root user, so please run "sudo -" to become root if you are logged in as a different user.
WARNING: The VNC protocol does not encrypt the transmitted data or login details, use a VPN tunnel if you plan to use it over a insecure or public network.
1. Installing Gnome
First we install some prerequisites for installing Ubuntu PPA repositories:
apt-get install software-properties-common
Then add the Gnome 3 PPA repository with this command:
add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-staging
Then, Press [ENTER] to proceed
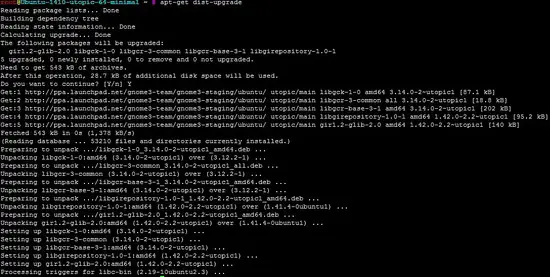
apt-get update
apt-get upgrade
2. Installing VNC
VNC (Virtual Network Computing), this is used for remote access software to control and this can be done by installing in destination server.
Diagram:
VNC client(source) -> Internet cloud -> VNC Server(destination)
VNC Destination server:
Assign a IP address
VNC server installed
Password set in VNC (for security purposes)
VNC Source client:
VNC viewer installed (you can install this to any client pc either your using windows or linux)
Here are the steps:
VNC client(source) -> Internet cloud -> VNC Server(destination)
VNC Destination server:
Assign a IP address
VNC server installed
Password set in VNC (for security purposes)
VNC Source client:
VNC viewer installed (you can install this to any client pc either your using windows or linux)
Here are the steps:
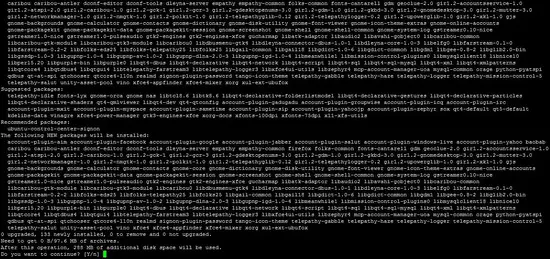
apt-get install gnome-core xfce4 firefox
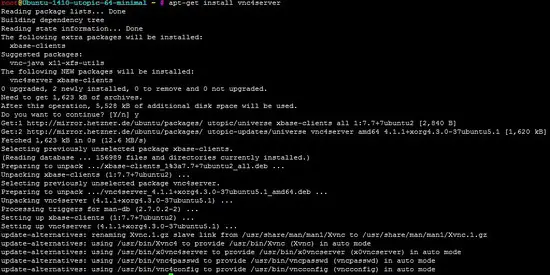
apt-get install vnc4server
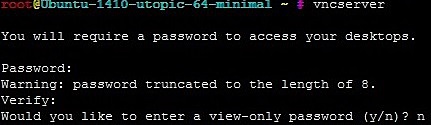
vncserver
If you seen this option view-only password, this means you have no control on remote server. So, in this case you will need to choose "n", so you have a full access.
Once its running, you may kill the process.
vncserver -kill :1
cp ~/.vnc/xstartup ~/.vnc/xstartup.bak
> ~/.vnc/xstartup
vi ~/.vnc/xstartup
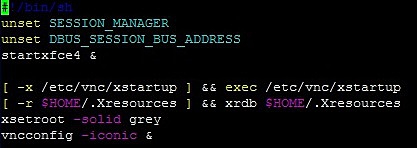
Insert this given data into the file xstartup.
for easier copy / pasting, here the content of the startup file as text
#!/bin/sh unset SESSION_MANAGER unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS startxfce4 & [ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup [ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources xsetroot -solid grey vncconfig -iconic &
Then make the startup file executable.
chmod +x xstartup
#!/bin/bash
unset VNCSERVERARGS
VNCSERVERS=""
[ -f /etc/vncserver/vncservers.conf ] && . /etc/vncserver/vncservers.conf
prog=$"VNC server"
start() {
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
REQ_USER=$2
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
ulimit -S -c 0 >/dev/null 2>&1
RETVAL=0
for display in ${VNCSERVERS}
do
export USER="${display##*:}"
if test -z "${REQ_USER}" -o "${REQ_USER}" == ${USER} ; then
echo -n "${display} "
unset BASH_ENV ENV
DISP="${display%%:*}"
export VNCUSERARGS="${VNCSERVERARGS[${DISP}]}"
su ${USER} -c "cd ~${USER} && [ -f .vnc/passwd ] && vncserver :${DISP} ${VNCUSERARGS}"
fi
done
}
stop() {
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
REQ_USER=$2
echo -n $"Shutting down VNCServer: "
for display in ${VNCSERVERS}
do
export USER="${display##*:}"
if test -z "${REQ_USER}" -o "${REQ_USER}" == ${USER} ; then
echo -n "${display} "
unset BASH_ENV ENV
export USER="${display##*:}"
su ${USER} -c "vncserver -kill :${display%%:*}" >/dev/null 2>&1
fi
done
echo -e "\n"
echo "VNCServer Stopped"
}
case "$1" in
start)
start $@
;;
stop)
stop $@
;;
restart|reload)
stop $@
sleep 3
start $@
;;
condrestart)
if [ -f /var/lock/subsys/vncserver ]; then
stop $@
sleep 3
start $@
fi
;;
status)
status Xvnc
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|condrestart|status}"
exit 1
esac
and make it executable.
chmod +x /etc/init.d/vncserver
mkdir -p /etc/vncserver
vi /etc/vncserver/vncservers.conf
Then insert this to vncserver.conf and make it root user in VNCSERVERS="1:root" (this will depend on what user are you gonna use)
VNCSERVERS="1:root"
VNCSERVERARGS[1]="-geometry 1024x768"
Now, will create to startup upon boot of the system.
update-rc.d vncserver defaults
reboot
Once the system up and running you may use any VNC client and configure it. (as with me i install TightVNC on my windows pc)
In this example, in VNC server -> <enter the ip address of the target server>:<port number>, since this VNC server is using port number 5901.











No comments:
Post a Comment